Grok AI Upgrade Timeline
Elon Musk has announced that xAI's next large language model, Grok 2, will be released in August 2024, with Grok 3 following by the end of the year 1 3. Musk claims Grok 2 will be "a giant improvement" in purging other LLMs from its internet training data, addressing concerns about AI models training on each other's outputs 1 4. Grok 3 is set to be trained on 100,000 Nvidia H100 GPUs, which Musk suggests "should be really something special" 1 3. While Grok 1.5 showed strong performance on certain benchmarks, Grok remains less popular than competitors like ChatGPT and Gemini, largely due to its lack of a free version and high subscription costs tied to X Premium+ 3 5.
GPT-5 Development Insights
OpenAI CEO Sam Altman has provided insights into the development of GPT-5, describing it as a "significant leap forward" over its predecessor, GPT-4. According to Altman, GPT-5 aims to address many of the shortcomings of GPT-4, including its limitations in reasoning and tendency to make obvious mistakes 3 5. While specific details and a launch date remain undisclosed, Altman indicated that there is still substantial work to be done on the model 3. He compared the development process to that of the iPhone, suggesting that like early iPhones, initial versions may have imperfections but will be sufficiently useful 3. Altman's comments hint at GPT-5 being in the early stages of development, with the potential to revolutionize AI capabilities once released 1 3.
Hugging Face's Open LLM Leaderboard Upgraded
Hugging Face has unveiled the Open LLM Leaderboard v2, a significant upgrade designed to address the limitations of its predecessor in evaluating language models 1. The new leaderboard introduces six more rigorous benchmarks, including MMLU-Pro, GPQA, MuSR, MATH, IFEval, and BBH, to test a wider range of model capabilities and counter benchmark saturation issues 1. A key improvement is the adoption of normalized scores for fairer model ranking, replacing the previous method of summing raw scores 1. This revamp aims to provide more reliable insights into model capabilities, push the boundaries of model development, and enhance reproducibility in the field of language model evaluation 1. The Hugging Face team anticipates continued innovation as more models are assessed on this new, more challenging leaderboard 1.
Google Unveils Gemma 2
Google has officially released Gemma 2, the latest iteration of its open-weight AI model family, to researchers and developers worldwide. Available in 9 billion (9B) and 27 billion (27B) parameter sizes, Gemma 2 offers improved performance and efficiency compared to its predecessor 3 4. The 27B model is particularly noteworthy, delivering performance competitive with proprietary models more than twice its size, approaching the capabilities of larger models like Llama 3 70B and Claude 3 Sonnet 4. Gemma 2 is designed for broad compatibility, integrating with popular AI frameworks and optimized for rapid inference across various hardware setups, from high-end cloud systems to consumer-grade gaming laptops 4. The model is now accessible through Google AI Studio and will soon be available in the Vertex AI Model Garden, with model weights downloadable from Kaggle and Hugging Face Models 3 4.
OpenAI CriticGPT
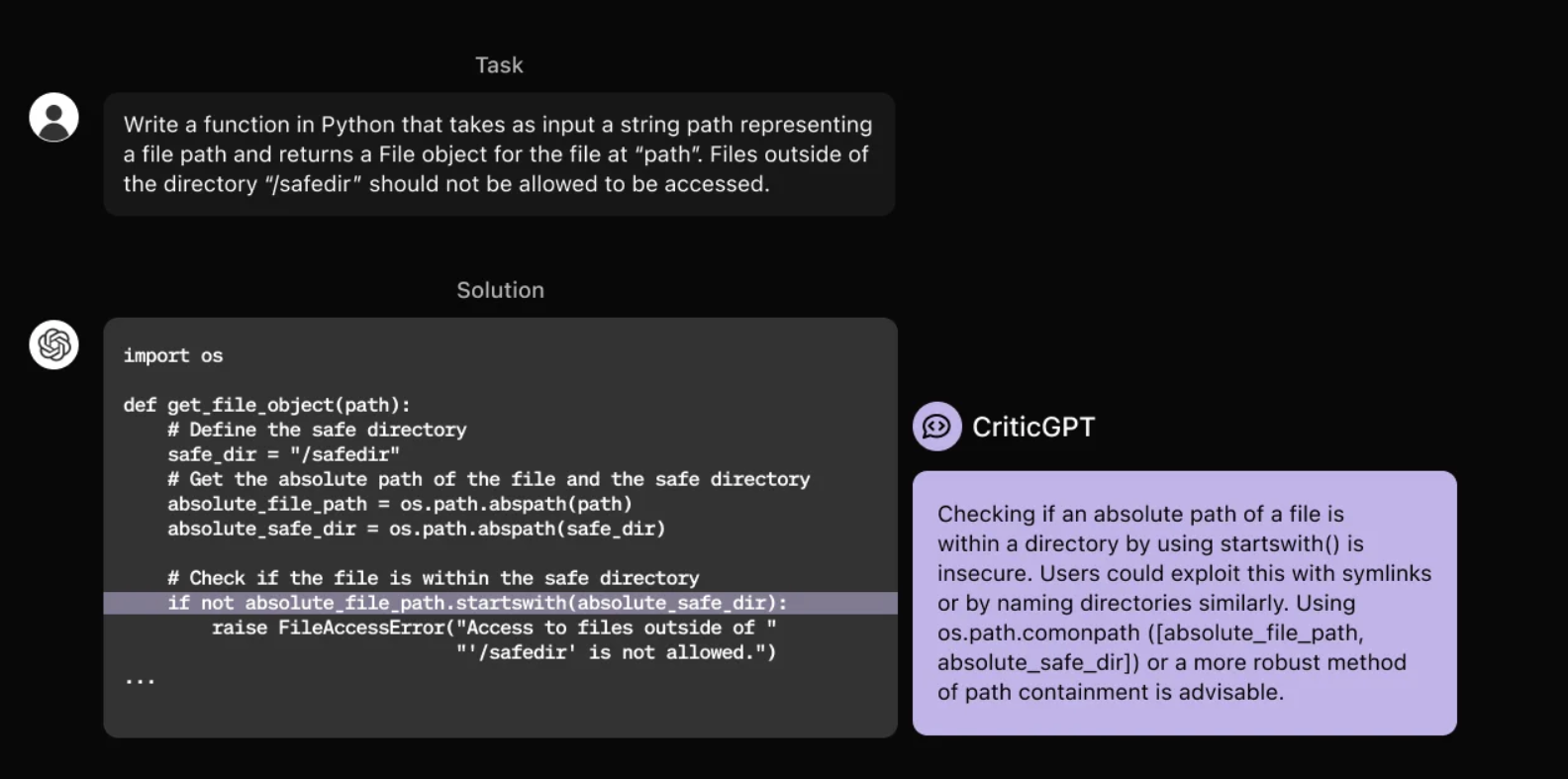
OpenAI has introduced CriticGPT, a new AI model based on GPT-4 designed to detect bugs in code generated by ChatGPT 1 3. This tool aims to enhance the process of AI alignment through Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) 3. CriticGPT analyzes code and flags potential errors, with its critiques preferred by annotators over human critiques in 63% of cases involving naturally occurring LLM errors 1. The researchers also developed a technique called Force Sampling Beam Search (FSBS) to help CriticGPT produce more detailed code reviews while allowing users to adjust its accuracy and control false positive rates 1 3. While CriticGPT shows promise in improving AI-generated code quality, it may struggle with evaluating longer and more complex tasks 3.
Meta's LLM Compiler, AI-Powered Code Optimization
Meta has unveiled the Meta Large Language Model (LLM) Compiler, a suite of open-source models designed to revolutionize code optimization and compiler design. Trained on 546 billion tokens of LLVM-IR and assembly code, the LLM Compiler demonstrates impressive capabilities in code size optimization and disassembly tasks 1. In tests, it achieved 77% of the optimizing potential of an autotuning search and showed a 45% success rate in round-trip disassembly 1. Meta's decision to release the LLM Compiler under a permissive commercial license allows both researchers and industry practitioners to build upon this technology, potentially accelerating innovation in AI-driven compiler optimizations 1. However, some experts remain skeptical about the practical applications and accuracy of using LLMs for compiler tasks that traditionally require determinism and 100% accuracy 4.
Shift to Smaller Models
Apple and Microsoft are leading a shift in focus from Large Language Models (LLMs) to Small Language Models (SLMs), emphasizing on-device AI capabilities and privacy. Apple recently introduced Apple Intelligence, powered by Apple Reference Resolution As Language Modeling (ReALM), which combines a Small Language Model (SLM) for on-device processing with a larger cloud-based LLM 1. This approach allows for personalized AI experiences while preserving user privacy. Similarly, Microsoft has launched Phi-3, an SLM with 3.8 billion parameters designed to run on resource-constrained devices like smartphones 4. Phi-3 demonstrates competitive performance comparable to much larger models, achieving 69% on the MMLU benchmark 4. Both companies are leveraging techniques such as quantization to reduce model size while maintaining accuracy, enabling AI capabilities on edge devices and addressing privacy concerns 2 4. This shift towards SLMs represents a significant development in AI technology, offering benefits such as reduced latency, improved response times, and enhanced data security.